MicroRNA Research: The Journey to the Nobel Prize 2024
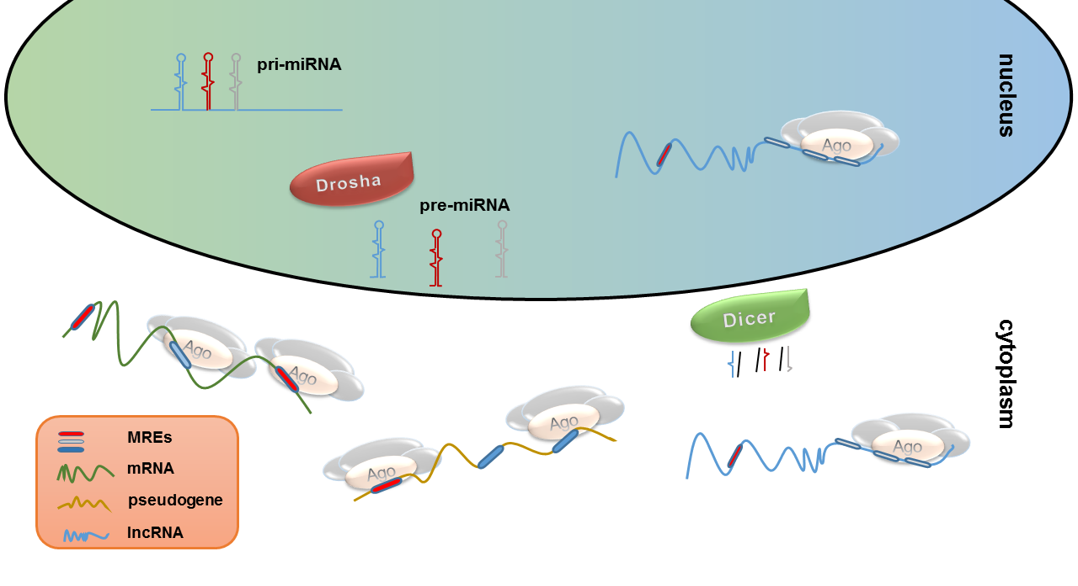
MicroRNA research has become a pivotal area of study in the field of genetics, illuminating the intricate mechanisms of gene regulation. Spearheaded by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun, whose groundbreaking findings in the C. elegans roundworm in 1992 revealed the significant role of microRNAs, this research has evolved into a vital component of modern biological science. As we approach the anticipated Nobel Prize 2024, it is essential to recognize how federal funding for science has propelled this research forward, encouraging exploration into the therapeutic potentials of microRNAs in diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. With emerging therapies entering clinical trials, the interest surrounding microRNA has attracted a diverse range of scientists, enhancing our understanding of organismal development and protein regulation across species. The impact of Ruvkun’s studies, supported by years of dedicated federal grants, showcases the intertwined relationship between revolutionary scientific discovery and robust governmental investment in research.
The exploration of small RNAs, particularly microRNAs, underscores a fundamental shift in our understanding of genetic expression and cellular function. Initially identified through studies in the C. elegans model organism, this research has generated a growing enthusiasm for its implications in various diseases and biological processes. As scientists delve deeper into the regulatory networks involving these tiny molecules, including their roles in gene silencing and modulation, related fields are increasingly recognizing the importance of such RNA components. This journey from niche exploration to broader applications illustrates how pivotal discoveries in genetics have the power to enhance our approach to medicine and biotechnology. In an era where federal grants are critical for sustaining scientific inquiry, the trajectory of small RNA research epitomizes the benefits of collaborative investment in innovative biological research.
The Impact of Gary Ruvkun’s Research on microRNA Discovery
In 1992, Gary Ruvkun, alongside Victor Ambros, embarked on a groundbreaking journey into the world of microRNA research, which would eventually earn them the prestigious Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024. Their pioneering work focused on understanding gene regulation in the C. elegans roundworm, a model organism that allowed them to explore the intricate roles these tiny RNA molecules play in cellular processes. Initially, their findings garnered little attention from the broader scientific community, but as the implications of microRNAs began to unfold, Ruvkun’s contributions became more valued and recognized.
The discovery of microRNAs revolutionized how scientists comprehend gene regulation, demonstrating that these small RNA molecules are not merely waste products but critical components in the developmental biology of multiple organisms, including humans. Ruvkun’s insistence on the importance of these molecular regulators has paved the way for ongoing research in various medical fields, leading to potential therapies for diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. This evolution emphasizes the significance of foundational research, showing that enduring dedication to uncovering biological mechanisms can transform into revolutionary advancements in medicine.
The Role of Federal Funding in Advancing Scientific Research
Throughout his career, Gary Ruvkun has emphasized the crucial role that federal funding has played in supporting his research endeavors. Over the past four decades, approximately 75% of his lab’s funding has come from the National Institutes of Health, amounting to around $150,000 annually. This funding not only supports salaries for highly educated staff members but also enables the lab to produce significant scientific breakthroughs in the understanding of microRNAs and their many applications in health and disease.
Ruvkun’s experience illustrates broader trends in scientific research, where federal funding serves as a backbone for achievements that contribute to the U.S.’s standing as a leader in the global scientific community. As the lives of young scientists depend on stable funding sources, Ruvkun warns that cuts to government support could jeopardize future discoveries and push skilled researchers to seek opportunities abroad, potentially stifling innovation and progress in critical scientific fields.
microRNA Research: A Fundamental Shift in Gene Regulation Understanding
The discovery of microRNAs by Gary Ruvkun and his colleagues has sparked a fundamental shift in our understanding of gene regulation. Initially met with skepticism, their research revealed that these tiny RNA molecules play a vital role in determining how genes are expressed within both simple organisms and humans. The insights gained from their work have led to the identification of approximately 1,000 distinct microRNAs in the human genome, each contributing to the regulation of protein-coding genes that are essential for various biological functions.
As the implications of these findings have grown, microRNA research has transitioned into a pivotal area of focus in molecular biology and medicine. Current research explores the potential of microRNAs in developing targeted therapies for a range of conditions, including heart disease and autoimmune disorders. The expanding interest in microRNA functions underscores the necessity for continued investment and innovation in this field, promising transformative results for therapeutic applications.
The Intersection of Basic Research and Pharmaceutical Development
Ruvkun’s research has not only advanced scientific understanding but has also laid the groundwork for successful pharmaceutical developments, particularly in RNA-based therapies. One notable example is Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, a company dedicated to discovering and commercializing RNA interference therapeutics. This success story highlights how basic research nurtured by federal funding can evolve into significant economic contributions, creating viable companies that tackle pressing medical issues while offering employment opportunities in the biotechnology sector.
The impact of Ruvkun’s work extends beyond the lab, illustrating how basic scientific discoveries can lead to practical applications that benefit society. As the pharmaceutical sector increasingly recognizes the value of microRNA research in drug design, collaboration between academia and industry becomes paramount. This partnership can accelerate the translation of fundamental discoveries into real-world solutions, reflecting the essential nature of continued investment in research and innovation.
Challenges and Future Directions in microRNA Research
Despite the impressive progress made in microRNA research, challenges remain that could impede future advancements. Ruvkun has expressed concerns about potential funding cuts and shifting priorities within federal research agencies, which could disrupt ongoing projects and lead to a loss of talent from the scientific workforce. As the understanding of microRNAs deepens, it is essential that investments are maintained to support the exploration of their roles in health and disease.
Looking ahead, the field of microRNA research promises to reveal even more complexities about gene regulation. Future studies may uncover novel microRNAs and their mechanisms, potentially unlocking new therapeutic avenues for previously intractable diseases. By facing these challenges head-on and advocating for continued federal support, researchers like Ruvkun can ensure that the field flourishes, leading to beneficial discoveries that may ultimately enhance human health.
The Community of Researchers and its Evolution
The evolution of the microRNA research community has been notable since Ruvkun and Ambros first published their findings in the early 1990s. Initially, their work attracted relatively little attention; however, as the field grew, interest surged among researchers from diverse areas, including molecular biology, genetics, and clinical sciences. This collective enthusiasm for microRNA studies has led to a collaborative environment where sharing knowledge and resources has accelerated advancements and innovative applications across disciplines.
Conferences and meetings that previously hosted modest participation have now become significant gatherings, reflecting the heightened awareness and appreciation for the implications of microRNA research. This sense of community fosters collaboration among scientists, which is critical for tackling complex biological questions and developing interdisciplinary approaches to solving health-related issues. As the microRNA landscape evolves, the interconnectivity of researchers will likely continue to shape the future of this transformative field.
The Long-term Benefits of Sustained Investment in Science
Sustained investment in scientific research has proven essential for fostering innovation and driving economic growth. As Ruvkun notes, much of his research has been backed by federal grants that provide a stable foundation for exploring novel scientific inquiries. This financial support is not merely an expense but an investment in the nation’s future—one that can yield long-term benefits through advancements in medicine, technology, and education.
Looking back at the post-World War II era, Ruvkun highlights how federal funding has enabled the U.S. to emerge as a powerhouse in scientific and technological innovation. The success stories stemming from this investment are evident in the rapid development of pharmaceutical companies and research institutions that operate at the forefront of science today. Thus, maintaining and increasing federal funding for scientific research is vital, ensuring that the next generation of breakthroughs continues to enhance public health and well-being.
Global Implications of microRNA Innovations
The innovations stemming from microRNA research are not just limited to the United States; they have global implications that could reshape healthcare systems worldwide. As therapies based on microRNAs enter clinical trials and demonstrate their efficacy in treating serious diseases, countries across the globe stand to benefit from these advances. The thoughtful application of microRNA-based technologies could lead to more effective treatments, minimize side effects, and ultimately deliver better patient outcomes on an international scale.
Moreover, as scientists in various countries embrace the potential of microRNA research, there is an opportunity for collaborative international studies that can expedite discoveries. These partnerships could facilitate the sharing of knowledge, resources, and expertise, enhancing the pace of innovation. Engaging the global scientific community in microRNA research reflects the interconnected nature of modern science, where the findings in one region can influence approaches and develop solutions worldwide.
The Future of Gene Regulation Studies Inspired by microRNA
The study of gene regulation has been profoundly transformed by the discovery and understanding of microRNAs. Ruvkun’s pioneering work continues to inspire new research directions that seek to decipher the complexities of gene networks. As scientists delve deeper into how microRNAs interact with other regulatory elements, the depth and breadth of knowledge about gene expression trajectories will expand, leading to critical insights in fields such as developmental biology and cancer research.
Future research may uncover not just the roles of known microRNAs but also the potential for discovering novel regulatory molecules that influence gene expression in unexpected ways. By leveraging innovative technologies, researchers can explore the intricate dynamics of gene regulation in real-time, potentially revealing patterns that could inform new therapeutic strategies. The legacy of Ruvkun’s work serves as a testament to the power of curiosity-driven science and the potential for continued exploration in the realm of molecular biology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do microRNAs play in gene regulation, as discovered by Gary Ruvkun?
Gary Ruvkun’s research on microRNAs uncovered a new level of gene regulation, particularly in the model organism C. elegans roundworm. These tiny RNA molecules are crucial for regulating the expression of genes, influencing how genes translate into proteins. Their discovery has revolutionized the understanding of genetic regulation and is fundamental to biological development and function.
How did federal funding contribute to advancements in microRNA research?
Federal funding, particularly from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), played a significant role in advancing microRNA research initiated by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros. Over the years, this financial support has enabled groundbreaking studies into microRNAs, expanding our understanding of gene regulation and leading to developments in therapies for diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
What are some potential therapeutic applications of microRNA research?
MicroRNA research has led to potential therapies for a variety of diseases, including heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Many of these therapies are currently in clinical trials, illustrating the significant impact that microRNAs can have on human health and disease management.
How has Gary Ruvkun’s discovery of microRNAs changed the scientific community’s approach to genetics?
Gary Ruvkun’s pioneering work on microRNAs has shifted the scientific community’s approach to genetic research, leading to increased interest in RNA biology across multiple fields. His discovery underscored the importance of these small RNA molecules in gene regulation, resulting in a broader acceptance and exploration of RNA roles in both humans and other organisms.
What impact has Gary Ruvkun’s research on microRNAs had on the biotechnology industry?
Gary Ruvkun’s research has significantly impacted the biotechnology industry, leading to the establishment of companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, which focuses on RNA interference therapeutics for genetic diseases. This demonstrates how foundational microRNA research can translate into commercial innovations and advancements in medical science.
Why is it important to continue funding microRNA research?
Continuing to fund microRNA research is vital to ensure ongoing discoveries that can lead to groundbreaking treatments for various diseases. As Gary Ruvkun highlights, federal funding has been instrumental in fostering scientific advancements that position the U.S. as a leader in biotechnology and health research.
What challenges does microRNA research face in securing federal funding?
MicroRNA research, despite its breakthroughs, faces challenges in securing consistent federal funding. Gary Ruvkun stresses that potential reductions in federal grants could deter young scientists from pursuing research careers, negatively impacting the future of innovations in genetic regulation and therapies based on microRNA.
How many microRNAs are identified in the human genome, and why are they important?
Studies have identified approximately 1,000 microRNAs within the human genome. These microRNAs are essential for regulating the majority of protein-coding genes, making them critical players in various biological processes, including cellular development and response to environmental changes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, revealing gene regulation in C. elegans. |
| Initial Reception | Their findings did not initially impress the evolutionary biology community, as the significance for other species was unclear. |
| Growth of Interest | Over time, interest in microRNAs grew significantly, leading to more attendees at scientific meetings and recognition of their role in various organisms. |
| Therapeutic Applications | MicroRNA therapies are being tested for conditions like heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Research Funding | About 75% of Ruvkun’s research was funded by federal government grants, enabling significant advancements in the field. |
| Economic Impact | Basic research has led to the formation of successful companies, such as Alnylam, highlighting the economic significance of microRNA research. |
| Future Concerns | Ruvkun expresses concerns over potential funding cuts which could drive young scientists away from research careers. |
Summary
MicroRNA research has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation and its implications in various diseases and therapies. From the initial discovery by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros to the current state of clinical trials, microRNAs have emerged as a crucial component in modern genetics. Continued support and investment in microRNA research are vital, as they pave the way for innovative treatments and enhance our comprehension of complex biological processes.